Unit testing DNX libraries with Xunit
Jürgen Gutsch - 15 December, 2015
DNX libraries are a bit special, there is no project file which handles references. There is no intuitive way to reference libraries and the result of a DNX library is a NuGet package.
A fact is, the a unit test project to test DNX libraries also needs to be a DNX library.
If I'm right, there are currently only two unit test libraries out there, which are supporting .NET Core. This are Xunit which I will show you in this post and and NUnit which is the topic in one of the next posts.
Reference a DNX library
Before we start to unit test, we need to know how to reference another DNX library.
BTW: There are two types of dependencies in a DNX Project, framework/platform specific which are added inside the framework definition and which are only available in that specific framework and global dependencies which will be available for all defined frameworks
Let's create two projects. The first one is the library we need to test and it contains a simple calculation class, with some methods to divide, multiply, and so on. The second project is our unit test project where we need to reference Xunit and our Library to test. We need to add a global dependencies node in the project json where we reference Xunit, the Xunit DNX runner, fluent assertions and our library
"dependencies": {
"UnitTestDemo": "",
"xunit": "2.1.0",
"xunit.runner.dnx": "2.1.0-*",
"FluentAssertions": "4.0.1"
},
Have a look how I referenced our library. If I don't add a version number it looks for a corresponding folder with a project.json inside. This is the way how we need to reference to another library. If the test library is not next to the library to test we need to add the path to the project.json.
BTW: The FluentAssertions which is used here is just a small helper to write nice and readable assert statements.
Writing tests
Writing tests is pretty common. You can use XUnit in the way you ever used it. For example write something like this:
[Fact]
public void Divide10By5ShouldResultIn2()
{
var expected = 2F;
var actual = Calculate.Devide(10, 5);
actual.Should().Be(expected);
}
[Fact]
public void DevideAnyNumberBy0ShouldResultInAnExeption()
{
Action act = () => Calculate.Devide(10, 0);
act.ShouldThrow<ArgumentOutOfRangeException>();
}
Running the tests
At first you need to add a new command to your unit test project:
"commands": {
"test": "xunit.runner.dnx"
},
This adds the command "test" which calls the Xunit runner. The runner is a DNX console application which gets the current library to test and executes all the unit tests inside.
Once you have compiled your project, you are able to use the unit test explorer in visual studio to run all the tests and to see the test results or you can just press "test" on the run menu in visual studio:
Using this, a console window pops up, does anything and closes. You don't see the any results. This guy runs the command you just created in the project.json and you can do it by your own, by using your favorite console.
Just cd to the directory of your test project, ensure you have all dependencies and start the command:
dnu restore
dnx test
This will show you the test results in the console:
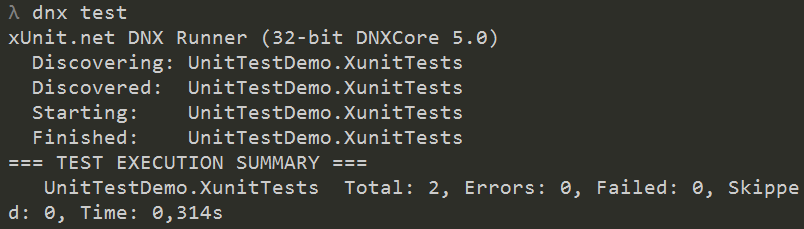
To create a test report into a file you only need to add the xunit runner arguments to the dnx command. You can just call dnx test tun run the unit test on a build server like AppVayor. On a Jenkins or on TFS you need to create test log which is readable by this systems.
